

^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar Mantina, Manjeera Chamberlin, Adam C.^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al A.^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch J.C.Data derived from other sources with different assumptions cannot be compared. The radius of an atom is not a uniquely defined property and depends on the definition.Such theoretical predictions are useful when there are no ways of measuring radii experimentally, if you want to predict the radius of an element that hasn't been discovered yet, or it has too short of a half-life. Experimental data on the other hand are only based on theories. However, often the empirical results then become an equation of estimation. Although, note that the values are not calculated by a formula. It basically means that you measured it through physical observation, and a lot of experiments generating the same results. Difference between empirical and experimental data: Empirical data basically means, "originating in or based on observation or experience" or "relying on experience or observation alone often without due regard for system and theory data".Covalent radius (Single-, double- and triple-bond radii, up to the superheavy elements.).These trends of the atomic radii (and of various other chemical and physical properties of the elements) can be explained by the electron shell theory of the atom they provided important evidence for the development and confirmation of quantum theory. The radius increases sharply between the noble gas at the end of each period and the alkali metal at the beginning of the next period.

For instance, the radii generally decrease rightward along each period (row) of the table, from the alkali metals to the noble gases and increase down each group (column). Ītomic radii vary in a predictable and explicable manner across the periodic table. Under some definitions, the value of the radius may depend on the atom's state and context.
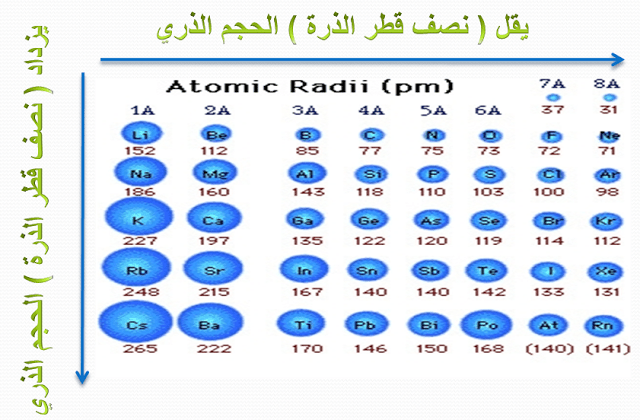
Depending on the definition, the term may apply only to isolated atoms, or also to atoms in condensed matter, covalently bound in molecules, or in ionized and excited states and its value may be obtained through experimental measurements, or computed from theoretical models. Since the boundary is not a well-defined physical entity, there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius. The atomic radius of a chemical element is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost shell of an electron.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
